ACCELERATE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT LAB GUIDE
API
Since modern application development has shifted to distributed, decoupled, and highly connected systems, every application needs to be appropriately and efficiently connected. The two most popular ways of connecting are through APIs and Events.
-
APIs simplify the way to connect applications using a well-understood and debuggable protocol. They have enabled the recent revolution that transformed the Digital Experience, being easier to reuse services, consume data, and as a result they have drastically sped up our ability to innovate.
-
Event Driven Architectures (EDA) give you near-real time latency, reduced service coupling, and ultimately provides better application encapsulation.
Red Hat accelerates the delivery of these two most widely adopted types of architecture by providing solutions the system needs. First the base platform, shifting from large monolithic applications to microservices means removing the complexity of managing day two operation, application delivery, and resource orchestration. In the previous sections, we got to witness how Red Hat can automate in a cloud native way and have code from the application in just a few minutes. Furthermore, we’re even able to deliver them in the form of containers to easily distribute and manage.
-
In the quarkus-superheroes-heroes_user project, select one of the rest-{“hero”, “villain”, “fight”} applications in the OpenShift Topology perspective and select the Resourcestab.
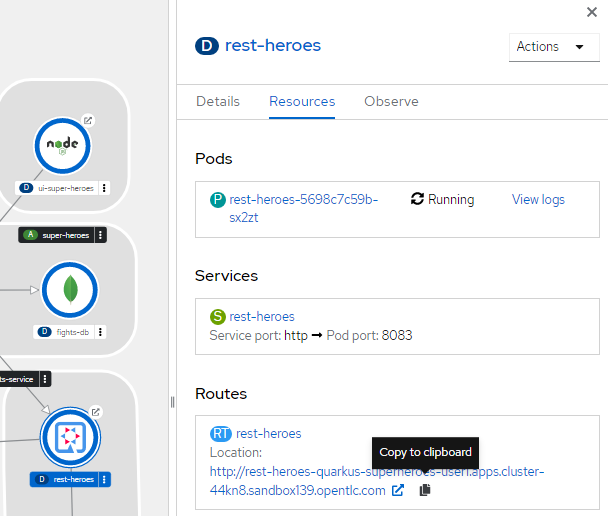
-
Copy the location under Routes and append /q/swagger-ui to the URL in your browser.
Note: If you receive an error of “Application is not available” in this step, it’s likely you’re using https which is default protocol for most browsers. We want to keep http here so keep the link as is when copied, and simply append /q/swagger-ui to the end of it.

-
Under {“heroes”, “villains”, “fights”}, expand one of the GET operations
-
Click on [Try It Out] and then on [Execute] and review the response back
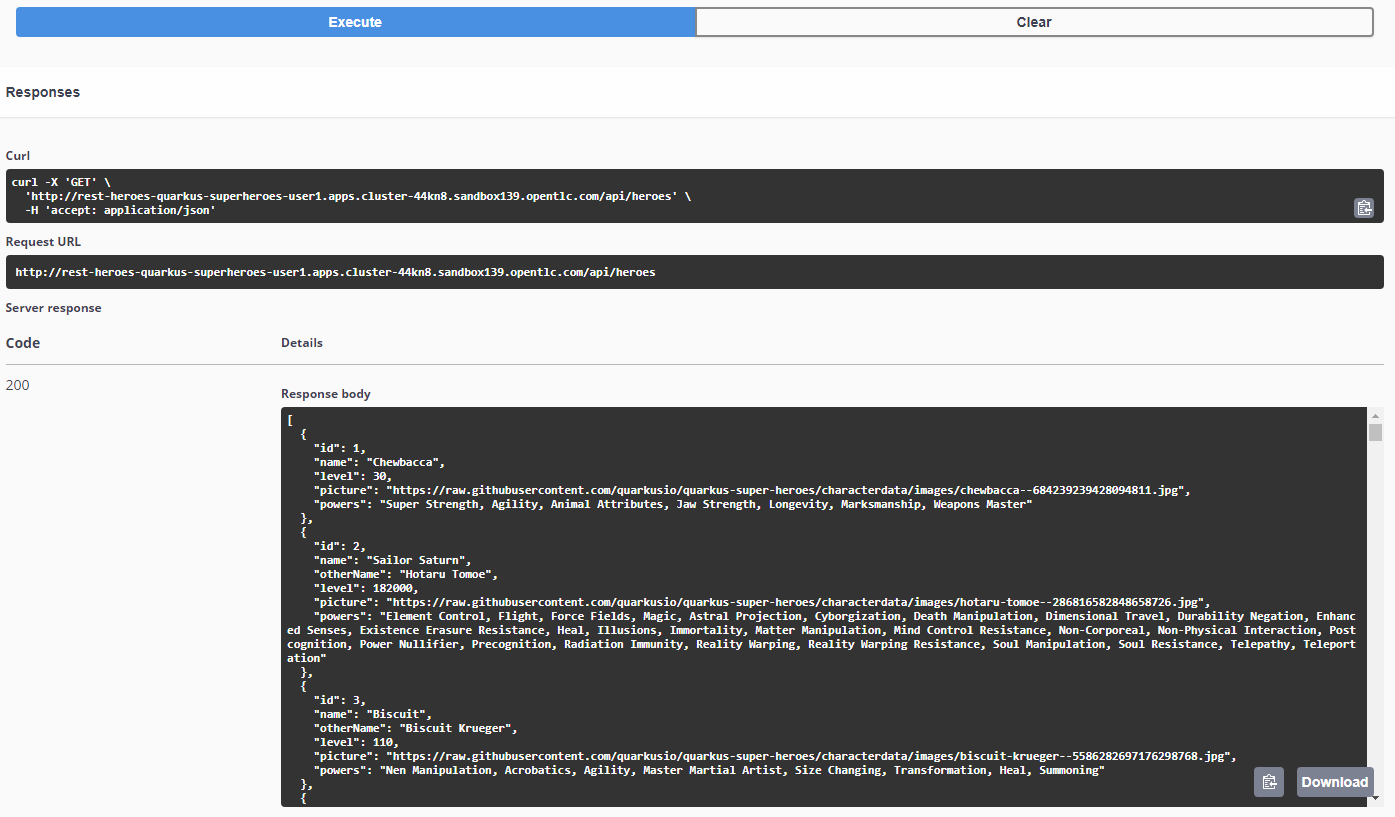
As a system grows, the API becomes another resource to manage as we have access control and security - all needing to be managed at greater scale, in order to provide consumers access to the service(s) you offer. (The same applies to endpoints in the event-driven world.)
All of the services in this demo, from the service handling a Fight, to the Villain and Hero services, are connected via API endpoints. To access the API service from each application, you can view the Swagger UI where it provides the OpenAPI schema that can be downloaded for consumers of the services.
FAULT TOLERANCE
In a distributed environment, fault tolerance happens around the clock for the maintainer, as they must allow it to partially run without bringing down the entire system. Otherwise, the system may result in cascading failures, where the failure of one service eventually brings down all of the services. This mechanism is built-in with Quarkus, and the developer can define how it should be handled. Examples include timeouts, fallbacks, retries, and circuit breakers.
-
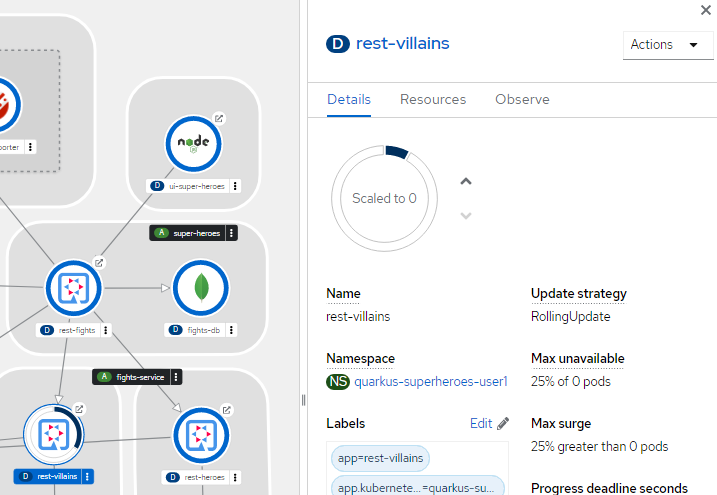
Back in Topology, find the rest-villains icon and click on it.
-
The deployment sidebar will appear on the right-hand side of the topology view. Click the Details tab.
-
Click the down arrow, next to the pod count chart, to scale the service down to 0 pods. This will simulate the service being unavailable.
-
Return to the Super Heroes UI and refresh the page, or click New Fighters.
Note: Please see the first section of Module 1 if you closed the UI and need help finding it again.
Note: There is about a 2 second delay and then the Super Heroes UI displays the Fallback villain
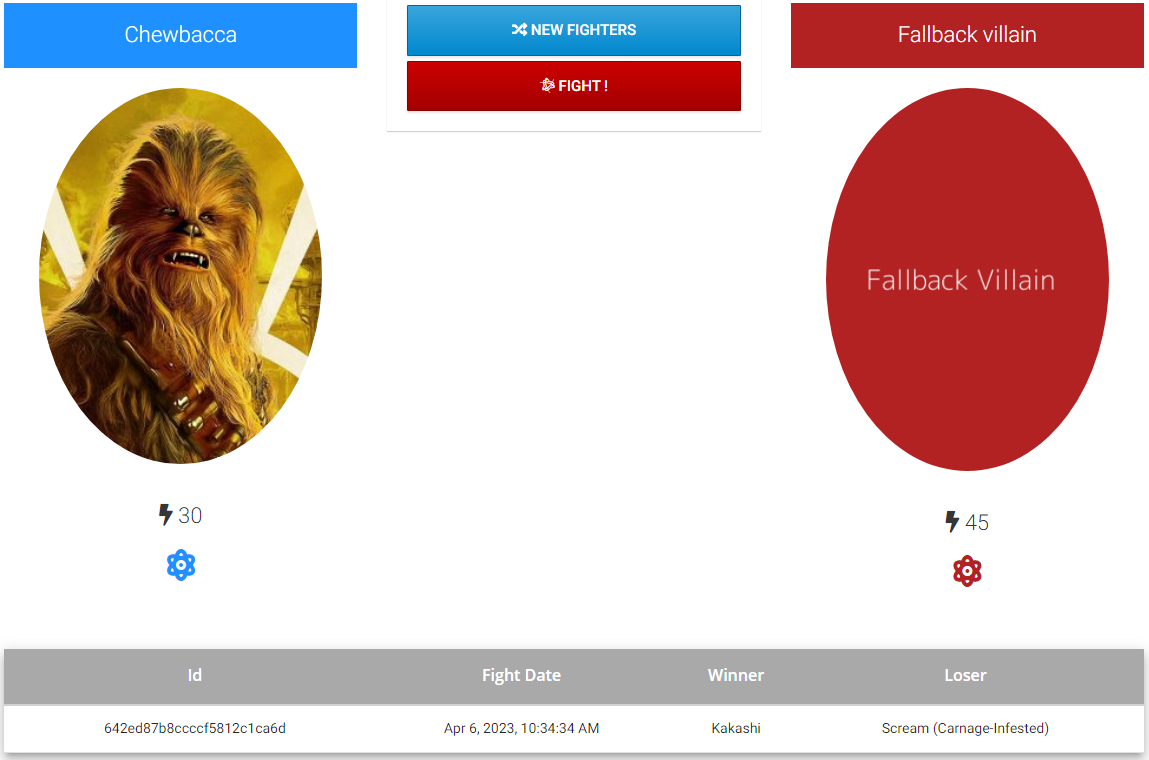
-
You can now reverse the procedure to scale the service back up.

-
Once it updates from “Scaling to 1 pod” to “1 pod”, return to the Super Heroes UI and refreshing the page should allow villains to appear again
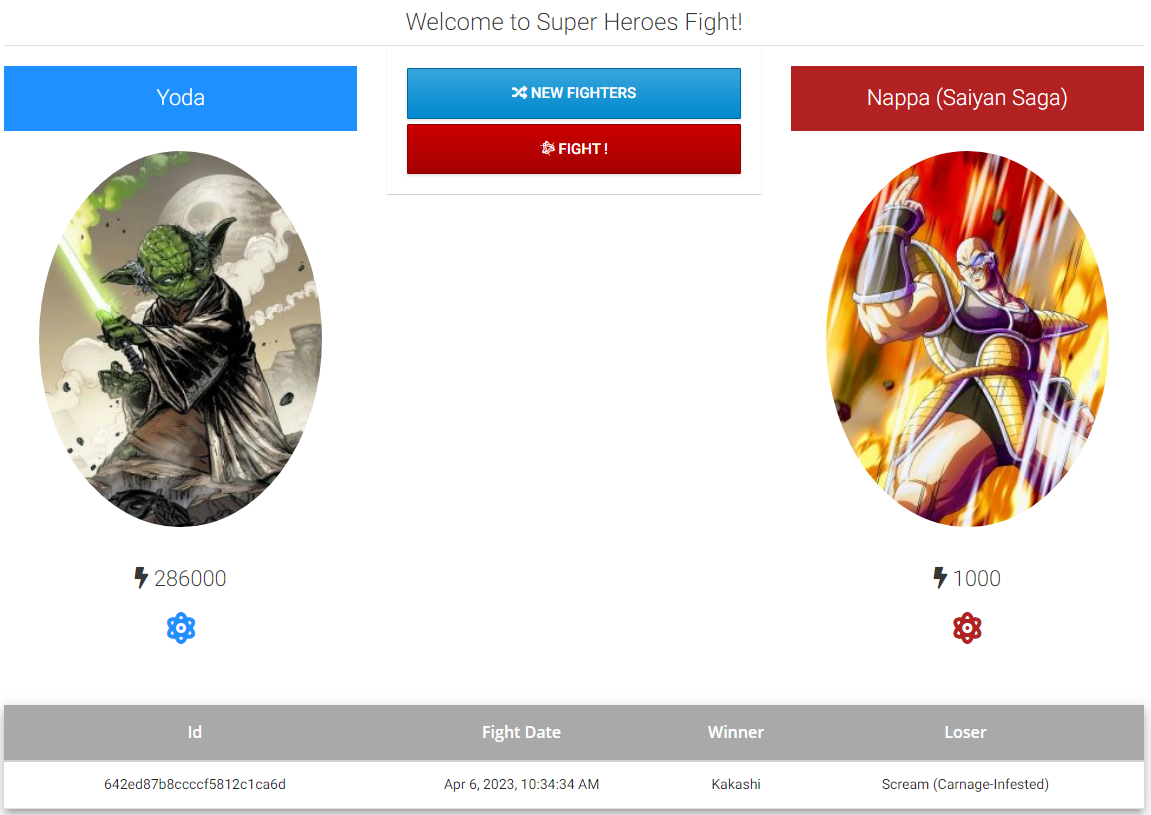
As you can see, the rest-fights service is resilient in the face of failures.
STREAMING WITH KAFKA
Event-driven architectures need a robust asynchronous communication backbone. Red Hat offers its very own cloud-native Kafka offering, which allows handling a large amount of throughput of events with reliable storage and ease of installation and maintenance.
-
Flip over to the Administrator Perspective in the top left hand corner of the OpenShift console.
Note: Admin rights are restricted in this lab instance, so you’ll only be able to review what’s in the current namespace, but when you go to review this on your own in the sales play demo, you’ll have access to administrator..
-
Select [Operators] on the left menu, and select [Installed Operators].
-
Select AMQ Streams.
-
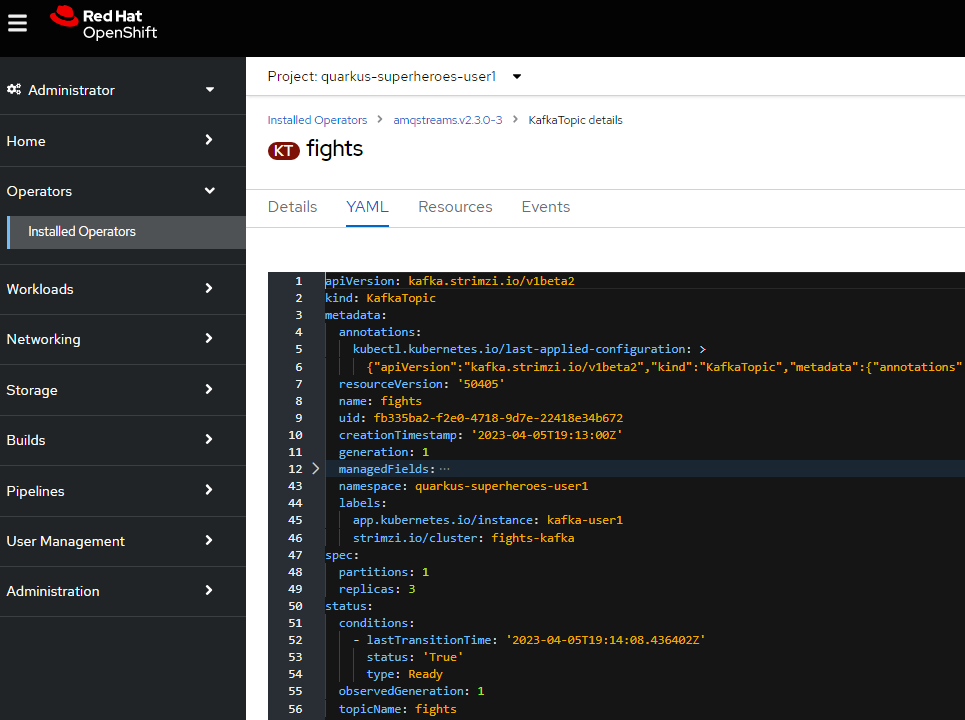
In the Kafka Topic tab, select Show operands in: Current namespace only.
-
Review some of the Kafka Topics by selecting them, and view installation details by clicking on their respective YAML tabs.
EVENT-DRIVEN ARCHITECTURE
Similar to API, EDA also needs to manage, secure, and provide access information to its consumer. Here you will see the full list of event endpoints as well as the data format of each one.
-
Service Registry is built on the Apicurio open source community project and is the tool we will be exploring in this section of the lab.
-
Navigate to the Apicurio instance that is deployed for your user.
-
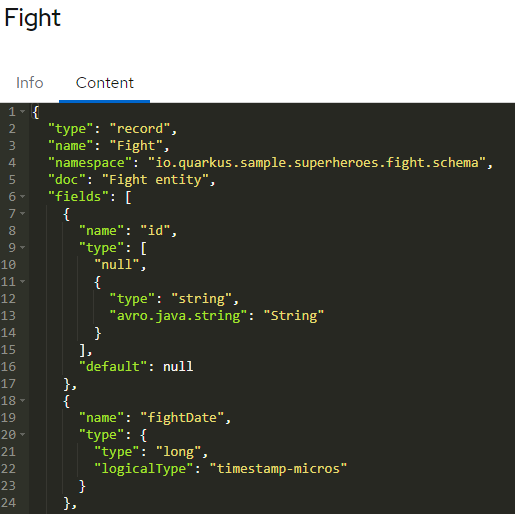
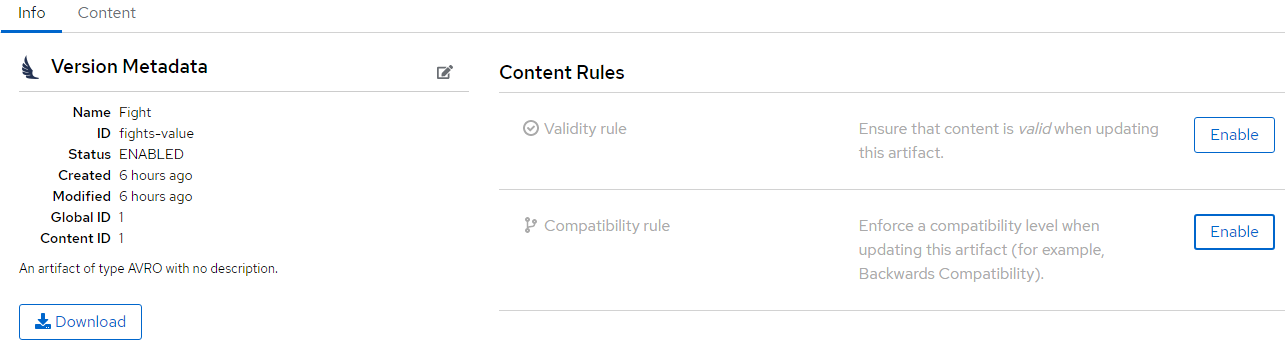
Select Fight (fights-value) to see more details and display general information about the schema.

Note: A Fight schema is automatically created after performing at least one fight. (If you’ve not yet, there won’t be any schemas in the registry)
-
Select Content to display the content of the schema.
-
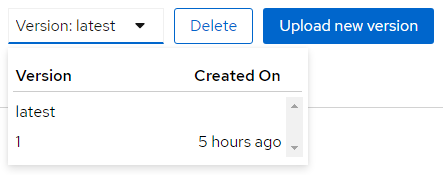
Select from the Version dropdown in the top right corner of the screen to display a particular version of the schema.
-
You can delete/upload new versions of the schema here and back on the info edit some of its metadata.
-
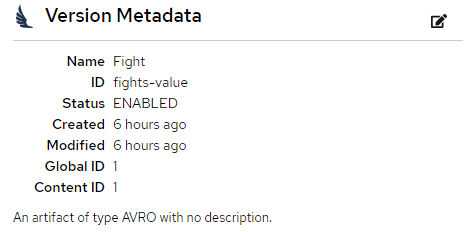
Select the edit icon next to Version Metadata to edit some of the metadata of the schema (Name/labels/description/etc).
-
As well, you can click [Download] to download the schema, [Enable] next to Validity rule to enable validation on the schema, or [Enable] next to Compatibility rule to enable compatibility rules when updating the schema.
Regardless of these two, the platform itself also has a complete set of supported services and applications. Check out the OperatorHub for the marketplace of all available partners in Red Hat’s OpenShift ecosystems.